Enhancing Cybersecurity for Small Businesses: Protecting Against Cyberattacks
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting your digital assets from unauthorized access, use, or damage by malicious actors. It is essential for small businesses because they often store sensitive data such as customer information, financial records, intellectual property, and trade secrets. Moreover, small businesses may rely on online platforms and services to operate and communicate with their customers, suppliers, and partners.
The Threat Landscape for Small Businesses
Small businesses are often more vulnerable to cyberattacks than their larger counterparts. According to a recent report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million, and small businesses suffered the highest per capita cost of $3,533 per employee.
Unmasking the Adversaries: Common Cyberattacks
Some of the common types of cyberattacks include:
- Phishing: A fraudulent email or message that tries to trick you into clicking on a malicious link or attachment or providing your personal financial information.
- Ransomware: A type of malware that encrypts your files or locks your device and demands a ransom to restore access.
- Malware: A generic term for any software that is designed to harm or disrupt your system or network, such as viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, etc.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) or distributed denial-of-service (DDoS): An attack that overwhelms your system or network with traffic or requests, making it slow or unavailable.
- Man-in-the-middle (MITM): An attack that intercepts or alters the communication between two parties, such as stealing your login credentials or tricking you into rerouting payments to the attacker’s bank account.
- SQL injection: An attack that exploits a vulnerability in your database by inserting malicious code that can execute commands, access data, or damage your database.
The Fallout: Consequences of Cyberattacks
The impacts of cyberattacks can be devastating for small businesses, such as:
- Loss of data: You may lose valuable or irreplaceable data that is essential for your business operations or reputation.
- Loss of access: You may experience downtime if your systems become unavailable due to an attack rendering you unable to do work.
- Loss of money: You may incur direct costs such as paying ransom, repairing damages, recovering data, or hiring experts. You may also lose revenue due to downtime, reduced productivity, or lost customers.
- Loss of trust: You may damage your relationship with your customers, suppliers, partners, or regulators who may lose confidence in your ability to protect their data or comply with their requirements.
- Loss of reputation: You may suffer negative publicity or legal consequences that can harm your brand, image, or market position.
The Imperative: Establishing an Effective Cybersecurity Program
A robust cybersecurity program is not only a necessity but also an opportunity for small businesses to gain a competitive edge and increase customer loyalty. A cybersecurity program is a systematic approach to managing your cybersecurity risks and improving your cybersecurity capabilities. It can help you:
- Identify and prioritize your cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities
- Implement and maintain effective cybersecurity controls and policies
- Detect and respond to cybersecurity events and incidents
- Comply with relevant laws and regulations
- Educate and train your employees and stakeholders on cybersecurity awareness and best practices
But how do you build a cybersecurity program for small businesses? Below are some steps you can follow.
Blueprint for Success: Building Your Cybersecurity Program
1. Assess your Current Cybersecurity Posture and Risks
Begin by understanding your cybersecurity standing and pinpointing gaps. Conduct a comprehensive assessment that evaluates your current cybersecurity practices, processes, tools, and resources against industry standards and best practices. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) cybersecurity framework serves as a valuable guide, helping you evaluate and enhance your cybersecurity across essential functions. The NIST framework is especially important for small and midsized defense contractors on their path to Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) compliance. NIST SP 800-30 is the publication that serves as a comprehensive guide for conducting risk assessments, specifically tailored to information technology systems and organizations.
You can also use tools such as our Free NIST 800-171 self-assessment tool and take advantage of our free risk assessments to help you measure your cybersecurity maturity level and identify areas for improvement
2. Define the Principles Behind Your Cybersecurity Program
The next step is to define the cybersecurity principles behind your program that align with your business strategy and vision. Questions to consider to guide your program principles are:
- Is it important for you to have employees travel and work from remote locations or home, or can you limit risk by having everyone work in an office?
- Do you have labs, prototyping facilities, or technical specialists that need broad access to different technologies, or can you standardize your tech stack?
- Do you need physical copies of sensitive data, or can you do everything digitally?
- Are there regulations you need to follow that govern the data you collect or receive from customers?
3. Implement Cybersecurity Best Practices and Standards
Embrace cybersecurity best practices and standards that address your cybersecurity risks and support your cybersecurity goals and objectives. Key practices include:
- Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication
- Regular antivirus updates
- Firewalls and secure access services
- Data backups and encryption
- Regular system and application patching
- Access limitation and network segregation
- An incident response and disaster recovery plan
4. Monitor and Measure your Cybersecurity Performance and Compliance
Monitor and measure your cybersecurity performance and compliance against your cybersecurity goals and objectives. A dashboard can help you track and visualize your cybersecurity metrics and indicators such as:
- Number of cybersecurity events and breaches
- Time to detect, contain, and resolve events
- Cost of events and breaches
- Number of vulnerabilities identified and remediated
- Compliance status
5. Improve your Cybersecurity Program Continuously
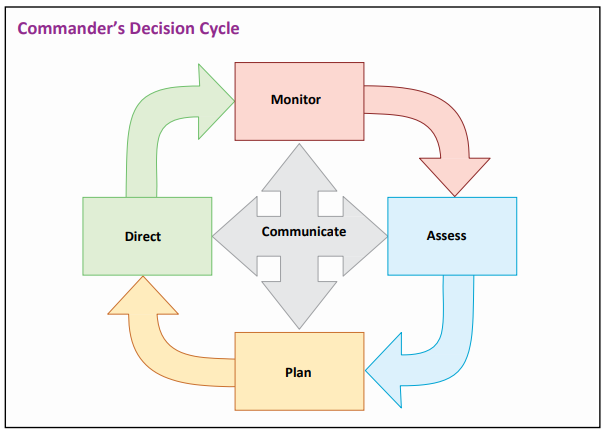
Based on your monitoring and measurement results, feedback, lessons learned, best practices, and emerging trends, continually enhance your cybersecurity program. Implement a commander’s decision cycle to help you make ongoing improvements.
How Ardalyst Can Help
Ardalyst’s Tesseract Managed Cybersecurity Program was built to help small and midsized businesses implement a comprehensive program to comply with regulatory requirements and improve your cybersecurity posture without the expensive price tag of most cybersecurity solutions on the market. Built on the NIST 800-171 framework, it helps defense contractors meet FAR and DFARS requirements, and helps any organization implement cybersecurity best practices. Get started today with our free options below:
- Get your free risk assessment. Meet the requirements for RA.L2-3.11.1 and lay out the foundation for your comprehensive cybersecurity program.
- Start your free Tesseract trial. Not only receive your free risk assessment but gain a free:
- Preview of your System Security Plan (SSP) & Plan of Actions and Milestones (POAM)
- An overview of the Tesseract Managed Cybersecurity Program and your path to getting & staying compliant
- A technical design of your Tesseract program enclave
- Exclusive deals on additional tools like Microsoft 365.
- Try our free NIST SP 800-171 Self-Assessment tool. Get everything you need totally free from your self-assessment score, compliance mapping, and score optimization.





